在历史上,基本的时间单元“秒”来自于地球围绕其轴心的自转。地球完成一次自转需要 24 个小时或者 24×60×60=86400 秒,如此看来如何精确定义秒只是一个天文测量问题。不幸的是,地球会轻微地摇晃,因而需要一种更精确的定义。在1967年,科学家们根据铯 133 原子的固有属性重新对“1秒”进行了精确的定义,同时也与历史定义相匹配。此后,官方时间一直由原子钟网络所保持。
1967年,国际计量大会对秒进行了重新定义:秒是铯-133原子基态的两个超精细能级之间跃迁所对应的辐射的 9192631770 个周期的持续时间。
在此之前,秒的定义曾借助天文观测,将地球自转的平均周期(即日长)细分成 86400 份来得到秒长。但由于地球自转存在周期性变化等原因,人们开始采用原子时。铯-133原子在特定条件下跃迁辐射的周期具有高度的稳定性,因此被选用来定义秒。
官方计时员经常需要将绝对时间与地球的自转同步。起初,官方秒钟会小幅度地调整,但从1972年开始,采取的措施改为偶尔插入“闰秒”(理论上,可能需要过一段时间删除一秒钟,但是这并没有发生过)。有传闻这个系统会被再次改变。显然,闰秒令人痛苦,因此许多计算机系统选择使用“更缓和”的方式,故意在闰秒前人为减少或增加时间,以保持每天为 86400 秒。这没问题,因为计算机上的本地时间并不会完全精确,而且计算机通常都会与一个外部的时间服务同步。
Java 日期和时间 API 规范要求 Java 使用如下时标:
每天都有 86400 秒。
每天正午与官方时间准确匹配。
其他时间也要以一种精确定义的方式与其紧密匹配。
这给 Java 带来了灵活性,即便将来官方时间发生变化,Java 也可以进行相应的调整。
java8 广告位
Instant 类
在 Java8 中,一个 Instant 对象表示时间轴上的一个点(基于原点的纳秒数)。Instant 是定义在 java.time 包中的一个类,它以正确的纳秒精度在时间轴上表示日期和时间。Instant 的值可以回退到 10 亿年前之久 (Instant.MIN)。Instant 的最大值 (Instant.MAX) 表示 1000000000 年的 12 月 31 日。Instant 静态方法 Instant.now() 会返回当前的瞬时点。你还可以使用 equals 和 compareTo 方法来比较两个瞬时点,以便将它们作为时间戳使用。
什么是原点?
原点 (我们也称之为“元年”) 被规定为 1970 年 1 月 1 日的午夜,此时本初子午线正在穿过伦敦格林威治皇家天文台。UNIX/POSIX 时间也使用了一样的约定。从原点开始,时间按照每天 86400 秒进行计算,向前向后分别以纳秒为单位。
Instant 类的作用主要包括以下几点:
处理和时间戳相关的操作:例如获取当前时间的时间戳、通过给定的时间戳创建 Instant 对象等。
时间的计算:可以进行时间的加减操作,如增加或减少一定的秒数、毫秒数、纳秒数等。
比较时间先后:Instant 提供了 isBefore() 和 isAfter() 方法来比较两个 Instant 对象的先后顺序,也可以使用 compareTo() 方法进行比较。
与其他日期时间类的转换:Instant 能够转换为 LocalDateTime、ZonedDateTime 等类,以便进行不同形式的时间表示和处理,例如结合时区信息。
时间戳的获取:通过 toEpochMilli() 方法可以获取从 1970 年 1 月 1 日 00:00:00 开始的毫秒数。
注意:Instant 类内部使用两个字段存储时间信息,一个是以秒为单位的时间戳,另一个是纳秒数(范围是 0 到 999,999,999),如下图:
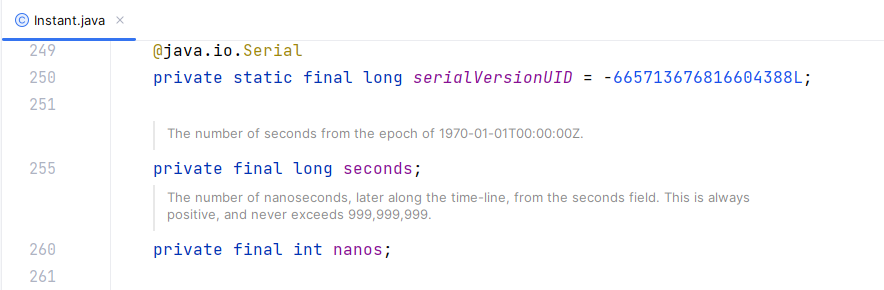
上图中,seconds 存储秒数,nanos 存储纳秒数。另外,Instant 类是不可变且线程安全的,这使得它在多线程环境中使用更加安全和可靠。
创建 Instant 对象
创建 Instant 对象的常见方式有:
例如:
package com.hxstrive.jdk8.date_time;
import java.time.Instant;
/**
* Instant 类
* @author hxstrive.com
*/
public class InstantDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取当前时间戳
Instant instant = Instant.now();
System.out.println(instant); // 2024-06-29T07:27:32.314583500Z
// 使用从 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z 开始的秒数获得一个 Instant 的实例
Instant instant2 = Instant.ofEpochSecond(100);
System.out.println(instant2); // 1970-01-01T00:01:40Z
// 使用从 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z 开始的毫秒数获得 Instant 的实例
Instant instant3 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(1500);
System.out.println(instant3); // 1970-01-01T00:00:01.500Z
}
}Instant 常用操作
以下是 Instant 类的一些常用方法:
now() 获取当前时间的 Instant 对象。
ofEpochMilli(long millis) 根据给定的毫秒时间戳创建 Instant 实例。
ofEpochSecond(long second) 根据给定的秒数时间戳创建 Instant 实例。
parse(String str) 从符合特定格式的字符串中创建 Instant 类型的时间,但字符串必须传入符合 UTC 格式的时间。
getEpochSecond() 获取 Instant 对象表示的总秒数。
toEpochMilli() 获取 Instant 对象表示的毫秒数。
getNano() 获取 Instant 对象中的纳秒数。
plus(Duration duration) 在当前Instant对象上加上指定的时间间隔(由 Duration 对象表示),返回一个新的 Instant 对象。例如:
minus(Duration duration) 或 minus(long amountToSubtract, TemporalUnit unit) 在当前 Instant 对象上减去指定的时间间隔,返回一个新的 Instant 对象。例如:
isAfter(Instant otherInstant) 判断当前 Instant 对象是否在另一个 Instant 对象之后。
isBefore(Instant otherInstant) 判断当前 Instant 对象是否在另一个 Instant 对象之前。
获取时间信息
下面示例将从 Instant 对象中获取秒数、毫秒数、纳秒数,例如:
package com.hxstrive.jdk8.date_time;
import java.time.Instant;
/**
* Instant 类
* @author hxstrive.com
*/
public class InstantDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Instant instant = Instant.now();
System.out.println(instant);
System.out.println("getEpochSecond=" + instant.getEpochSecond());
System.out.println("toEpochMilli=" + instant.toEpochMilli());
System.out.println("getNano=" + instant.getNano());
}
//输出:
//2024-06-29T07:44:24.740201600Z
//getEpochSecond=1719647064
//toEpochMilli=1719647064740
//getNano=740201600
}时间操作
下面示例将使用 Instant 进行时间的加法和减法操作,例如:
package com.hxstrive.jdk8.date_time;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.Instant;
/**
* Instant 类
* @author hxstrive.com
*/
public class InstantDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Instant instant = Instant.now();
System.out.println("原始值:" + instant);
// 在当前时间上添加 5 小时 4 分钟
Instant instant2 = instant.plus(Duration.ofHours(5).plusMinutes(4));
System.out.println("添加后:" + instant2);
// 在当前时间上减去 5 小时 4 分钟
Instant instant3 = instant.minus(Duration.ofHours(5).plusMinutes(4));
System.out.println("减去后:" + instant3);
Instant instant4 = instant.minusSeconds(80);
System.out.println("减去80秒后:"+ instant4);
Instant instant5 = instant.minusMillis(8000);
System.out.println("减去8000毫秒后:"+ instant5);
Instant instant6 = instant.minusNanos(8000000);
System.out.println("减去8000000纳秒后:"+ instant6);
}
//输出:
//原始值:2024-06-29T07:55:12.168308100Z
//添加后:2024-06-29T12:59:12.168308100Z
//减去后:2024-06-29T02:51:12.168308100Z
//减去80秒后:2024-06-29T07:53:52.168308100Z
//减去8000毫秒后:2024-06-29T07:55:04.168308100Z
//减去8000000纳秒后:2024-06-29T07:55:12.160308100Z
}java8 广告位
Instant 转换
Instant 与 java.util.Date 转换
Instant 转 java.util.Date,可以利用 Date 类的静态方法 from(Instant instant)。java.util.Date 转 Instant,使用 Date 类的 toInstant() 方法。例如:
Instant instant = Instant.now();
System.out.println("instant=" + instant);
// 将 Instant 转换为 Date 对象
Date date = Date.from(instant);
System.out.println("date=" + date);
// 将 Date 转换为 Instant 对象
Instant instant2 = date.toInstant();
System.out.println("instant2=" + instant2);
//输出:
//instant=2024-06-29T07:59:33.848345100Z
//date=Sat Jun 29 15:59:33 CST 2024
//instant2=2024-06-29T07:59:33.848ZInstant 与 LocalDateTime 转换
Instant 转 LocalDateTime,可通过 atZone(ZoneId zone) 方法先关联时区,再转换为 LocalDateTime。还可通过 toInstant(ZoneOffset offset) 方法将 LocalDateTime 转换为 Instant。例如:
Instant instant = Instant.now();
// Instant 转 LocalDateTime
ZoneId zone = ZoneId.systemDefault();
LocalDateTime localDateTime = instant.atZone(zone).toLocalDateTime();
System.out.println(localDateTime);
//2024-06-29T16:04:14.437173900
// LocalDateTime 转 Instant
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = LocalDateTime.now();
ZoneOffset offset = ZoneOffset.ofHours(8);
Instant instant2 = localDateTime2.toInstant(offset);
System.out.println(instant2);
//2024-06-29T08:06:57.977839800Z
Instant 与 ZonedDateTime 转换
Instant 转 ZonedDateTime,可以使用 atZone(ZoneId zone) 方法。ZonedDateTime 转 Instant,使用 toInstant() 方法,例如:
Instant instant = Instant.now();
// Instant 转 ZonedDateTime
ZoneId zone = ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai");
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = instant.atZone(zone);
System.out.println(zonedDateTime);
//2024-06-29T16:14:06.210674400+08:00[Asia/Shanghai]
// ZonedDateTime 转 Instant
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime2 = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
Instant instant2 = zonedDateTime2.toInstant();
System.out.println(instant2);
//2024-06-29T08:14:06.243656500ZInstant与长整型(long)转换
Instant 转长整型(以毫秒为单位),使用 toEpochMilli() 方法。长整型(以毫秒为单位)转 Instant,通过 ofEpochMilli(long millis) 方法创建 Instant 对象。例如:
Instant instant = Instant.now();
// Instant转长整型(以毫秒为单位)
long millis = instant.toEpochMilli();
System.out.println(millis);
//1719648944376
// 长整型(以毫秒为单位)转Instant
long millis2 = 1668350834000L;
Instant instant2 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(millis2);
System.out.println(instant2);
//2022-11-13T14:47:14Z
Instant 其他方法
query 方法
Instant 类的 query(TemporalQuery query) 方法用于在给定的时间查询对象的帮助下查询 Instant 对象。query 是一个非静态方法,只能通过类对象访问。该方法在查询对象时可能会引发异常。其中,参数 TemporalQuery query 表示用于查询该对象的查询对象。返回值的类型为 Result ,它返回由给定查询对象定义的查询结果。
如使用 TemporalQueries.precision() 来查询 Instant 的精度,例如:
Instant instant = Instant.now();
// 查询 Instant 的精度
String query = instant.query(TemporalQueries.precision()).toString();
System.out.println(query); // Nanos
truncatedTo 方法
Instant 类的 truncatedTo(TemporalUnit unit) 方法用于获取一个 Instant 对象,该对象保留了原始 Instant 对象的值,并将其截断到给定的时间单位。
注意:该方法在截断时可能会引发异常,例如当给定的单位由于无效而无法截断时,可能引发 DateTimeException;当不支持给定的单位时,可能发 UnsupportedTemporalTypeException。
方法的参数 TemporalUnit unit 表示要将 Instant 截断到的时间单位,例如 ChronoUnit.SECONDS(秒)、ChronoUnit.MINUTES(分钟)、ChronoUnit.HOURS(小时)、ChronoUnit.DAYS(天)等。
truncatedTo 方法将返回一个截断到给定单位后的 Instant 对象。例如:
package com.hxstrive.jdk8.date_time;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
/**
* Instant 类
* @author hxstrive.com
*/
public class InstantDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取当前时间的 Instant 对象
Instant now = Instant.now();
// 将 Instant 对象截断到秒
Instant truncatedToSeconds = now.truncatedTo(ChronoUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("截断到秒: " + truncatedToSeconds);
// 将 Instant 对象截断到分钟
Instant truncatedToMinutes = now.truncatedTo(ChronoUnit.MINUTES);
System.out.println("截断到分钟: " + truncatedToMinutes);
// 将 Instant 对象截断到小时
Instant truncatedToHours = now.truncatedTo(ChronoUnit.HOURS);
System.out.println("截断到小时: " + truncatedToHours);
// 将 Instant 对象截断到天
Instant truncatedToDays = now.truncatedTo(ChronoUnit.DAYS);
System.out.println("截断到天: " + truncatedToDays);
}
//输出:
//截断到秒: 2024-06-29T08:39:47Z
//截断到分钟: 2024-06-29T08:39:00Z
//截断到小时: 2024-06-29T08:00:00Z
//截断到天: 2024-06-29T00:00:00Z
}在上述示例中,首先获取了当前时间的 Instant 对象,然后分别将其截断到秒、分钟、小时和天,并打印出截断后的结果。
until 方法
Instant 类的 until(Temporal endExclusive, TemporalUnit unit) 方法用于计算两个 Instant 对象之间的时间间隔。它接受两个参数,endExclusive 表示结束时间(不包括在内),会被转换为Instant,unit 表示时间单位。
该方法会返回一个长整型数值,代表两个时刻之间的完整单位数。如果结束时间在开始时间之前,结果将为负。
该方法可能会抛出以下异常:
DateTimeException:如果给定的时态无法转换为 Instant。
UnsupportedTemporalTypeException:如果不支持给定的时间单位。
ArithmeticException:如果发生数字溢出。
以下是一个使用 until() 方法的示例代码:
package com.hxstrive.jdk8.date_time;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
/**
* Instant 类
* @author hxstrive.com
*/
public class InstantDemo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建两个 Instant 对象
Instant instant1 = Instant.parse("2024-06-29T16:00:00.00Z");
Instant instant2 = Instant.parse("2024-06-29T17:30:00.00Z");
// 计算两个 Instant 之间的分钟数
long minutes = instant1.until(instant2, ChronoUnit.MINUTES);
System.out.println("分钟数: " + minutes);
// 计算两个 Instant 之间的小时数
long hours = instant1.until(instant2, ChronoUnit.HOURS);
System.out.println("小时数: " + hours);
}
//输出:
//分钟数: 90
//小时数: 1
}在上述示例中,首先创建了两个 Instant 对象来表示不同的时间点,然后使用 until() 方法分别计算它们之间的分钟数和小时数。
with() 方法
Instant 类的 with(TemporalField field, long newValue) 方法用于创建一个新的 Instant 对象,该对象基于当前对象,但指定的时间字段的值被设置为新的值。其中:
以下是一个示例代码:
Instant instant = Instant.now();
// 修改秒内的纳秒数为 500000000
Instant newInstant1 = instant.with(ChronoField.NANO_OF_SECOND, 500000000);
// 修改秒内的毫秒数为 500
Instant newInstant2 = instant.with(ChronoField.MILLI_OF_SECOND, 200);
System.out.println("原始 Instant: " + instant);
System.out.println("修改纳秒后的 Instant: " + newInstant1);
System.out.println("修改秒内毫秒数后的 Instant: " + newInstant2);
//输出:
//原始 Instant: 2024-06-29T09:04:16.036427600Z
//修改纳秒后的 Instant: 2024-06-29T09:04:16.500Z
//修改秒内毫秒数后的 Instant: 2024-06-29T09:04:16.200Zwith 方法源码如下:
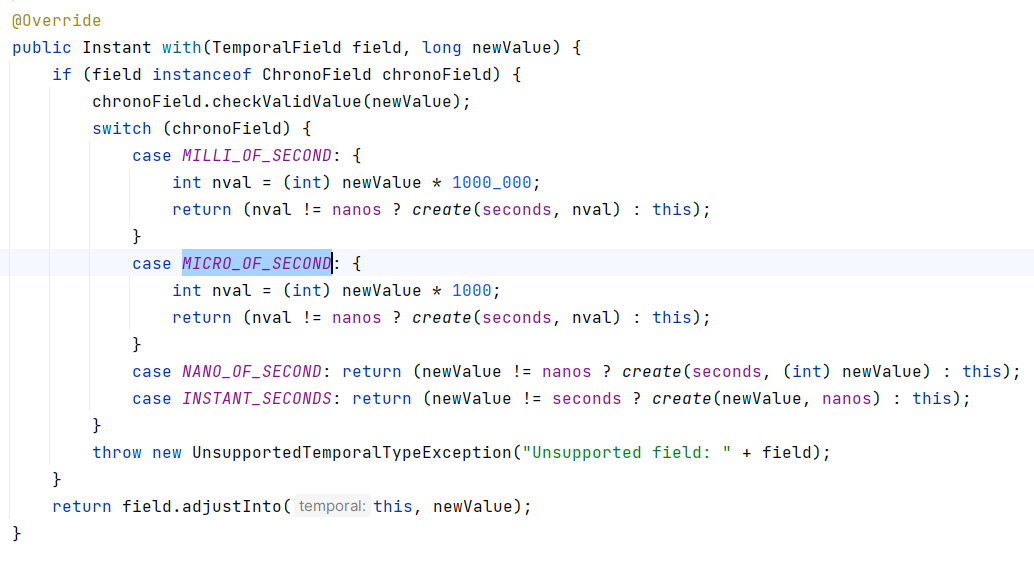
with(TemporalAdjuster adjuster) 方法用于根据指定的 TemporalAdjuster 对象来调整时间类对象的日期或时间。TemporalAdjuster 是一个接口,它定义了如何对时间进行调整的方法。通过传入不同的 TemporalAdjuster 实现,可以实现各种灵活的时间调整操作,例如:
Instant instant = Instant.now();
// 将日期的毫秒数调整为 500
Instant adjustedInstant = instant.with(new TemporalAdjuster() {
@Override
public Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal) {
return temporal.with(ChronoField.MILLI_OF_SECOND,500);
}
});
System.out.println("原始 Instant: " + instant);
System.out.println("调整后的 Instant: " + adjustedInstant);
//输出:
//原始 Instant: 2024-06-29T09:32:35.020071200Z
//调整后的 Instant: 2024-06-29T09:32:35.500Z





