本章将开始简单的分析 Eureka 源码,查看它的启动过程,它是怎样注册、续约、服务同步等。
前面章节介绍了 Eureka 的基础用法,本章将开始简单的分析 Eureka 源码,查看它的启动过程,它是怎样注册、续约、服务同步等。下面是 Spring Cloud 对应的 Spring Boot 版本信息:
| Spring Cloud 版本 | Spring Boot 版本 |
| 2020.0.x aka Ilford | 2.4.x |
| Hoxton | 2.2.x, 2.3.x (Starting with SR5) |
| Greenwich | 2.1.x |
| Finchley | 2.0.x |
| Edgware | 1.5.x |
| Dalston | 1.5.x |
本文分析的源码版本信息如下:
其中,涉及的 jar 包名称和版本如下:
Eureka 分为服务端(Eureka server)和客户端(Eureka client)。服务端就是注册中心,注册到服务端的服务实例称为客户端;客户端可以是服务提供者、也可是服务消费者。服务端也会向另一个服务端实例注册自己的信息,从而实现 Eureka server 集群。
springcloud广告位
Eureka Client 启动过程
启动服务需要添加 @EnableDiscoveryClient 或 @EnableEurekaClient 注解,从 Spring Cloud Edgware 开始,可省略这两个注解,只需在 classpath 上存在 Eureka 相关依赖,并进行相应配置,即可将微服务注册到服务发现组件上。
@EnableDiscoveryClient 和 @EnableEurekaClient 共同点是让注册中心能够发现,扫描到该服务。不同点是 @EnableEurekaClient 注解只适用于 Eureka 作为注册中心,而 @EnableDiscoveryClient 可以是其他注册中心。
下面开始分析源码:
(1)@EnableDiscoveryClient
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableDiscoveryClient {
// 控制 ServiceRegistry 是否自动注册本地服务,默认为 true
boolean autoRegister() default true;
}上面源码中,@Import 注解是将指定的 Bean 加入到 IOC 容器之中进行管理,ImportSelector 接口有一个 selectImports 方法,该方法将返回一个数组,也就是类实例名称,@Import 注解将会把 selectImports 方法返回的 Bean 加入到 IOC 容器中进行管理。
我们下面进一步分析 EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector 类的源码。
(2)EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector
@Order(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 100)
public class EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector extends SpringFactoryImportSelector<EnableDiscoveryClient> {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
// 1.核心功能在这里,获取需要注册到 Spring 的类
String[] imports = super.selectImports(metadata);
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationAttributes
.fromMap(metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(getAnnotationClass().getName(), true));
// autoRegister 为 @EnableDiscoveryClient 注解的属性
boolean autoRegister = attributes.getBoolean("autoRegister");
// 2.autoRegister默认为true,同时则注册AutoServiceRegistrationConfiguration类到Spring中
if (autoRegister) {
List<String> importsList = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(imports));
importsList.add("org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AutoServiceRegistrationConfiguration");
imports = importsList.toArray(new String[0]);
}
else {
Environment env = getEnvironment();
if (ConfigurableEnvironment.class.isInstance(env)) {
ConfigurableEnvironment configEnv = (ConfigurableEnvironment) env;
LinkedHashMap<String, Object> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put("spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled", false);
MapPropertySource propertySource = new MapPropertySource("springCloudDiscoveryClient", map);
configEnv.getPropertySources().addLast(propertySource);
}
}
return imports;
}
@Override
protected boolean isEnabled() {
// 默认为 true,在父类的 selectImports() 方法中会用到
// if (!isEnabled()) { return new String[0]; }
return getEnvironment().getProperty("spring.cloud.discovery.enabled", Boolean.class, Boolean.TRUE);
}
@Override
protected boolean hasDefaultFactory() {
return true;
}
}继续进一步分析 super.selectImports(metadata) 语句,这里的 selectImports() 方法实际在 SpringFactoryImportSelector 抽象类中,代码如下:
public abstract class SpringFactoryImportSelector<T>
implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware {
//...
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected SpringFactoryImportSelector() {
this.annotationClass = (Class<T>) GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(this.getClass(),
SpringFactoryImportSelector.class);
}
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
// enabled 默认值为 true,见子类 EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector 的 isEnabled() 方法
if (!isEnabled()) {
return new String[0];
}
//...
// Find all possible auto configuration classes, filtering duplicates
// 查找所有可能的自动配置类,过滤重复项
List<String> factories = new ArrayList<>(new LinkedHashSet<>(
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.annotationClass, this.beanClassLoader)));
//...
if (factories.size() > 1) {
// 只能有一个DiscoveryClient,但可能有多个工厂
this.log.warn("More than one implementation " + "of @" + getSimpleName()
+ " (now relying on @Conditionals to pick one): " + factories);
}
return factories.toArray(new String[factories.size()]);
}
//...
}进一步分析上面源码中的 SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames() 方法,源码如下:
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
// 使用给定的类加载器从 FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION 加载给定类型的工厂实现的标准类名称。
// 从Spring Framework 5.3开始,如果多次发现给定工厂类型的特定实现类名称,则将忽略重复项。
return loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
// classLoader 类型为 Launcher$AppClassLoader@1713
Map<String, List<String>> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
result = new HashMap<>();
try {
// FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION 是一个常亮,定义如下:
// public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
// urls 类型为 CompoundEnumeration@1737
// 查找拥有 FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION 文件的 jar 文件列表
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION);
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
// spring-boot-2.4.2.jar 文件,它包含了 META-INF/spring.factories
// jar:file:/D:/repository/maven/org/springframework/boot/spring-boot/2.4.2/spring-boot-2.4.2.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
// 解析 META-INF/spring.factories 属性文件
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
// 属性key,如:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
// 属性值,一个列表
String[] factoryImplementationNames =
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue());
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, key -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
// Replace all lists with unmodifiable lists containing unique elements
// 将所有列表替换为包含唯一元素的不可修改列表
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> implementations.stream().distinct()
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList)));
cache.put(classLoader, result);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
return result;
}spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-client-3.0.0.jar 中的 spring.factories,内容如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaClientConfigServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.DiscoveryClientOptionalArgsConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.reactive.EurekaReactiveDiscoveryClientConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerEurekaAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaConfigServerBootstrapConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.Bootstrapper=\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaConfigServerBootstrapper
将以上类注册到 Spring 容器中,EurekaClient 的关键功能就在 EurekaClientConfigServerAutoConfiguration 中,下面我们一起来看下这个类:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties
@ConditionalOnClass({ EurekaInstanceConfigBean.class, EurekaClient.class, ConfigServerProperties.class })
public class EurekaClientConfigServerAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired(required = false)
private EurekaInstanceConfig instance;
@Autowired(required = false)
private ConfigServerProperties server;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
if (this.instance == null || this.server == null) {
return;
}
String prefix = this.server.getPrefix();
if (StringUtils.hasText(prefix) && !StringUtils.hasText(this.instance.getMetadataMap().get("configPath"))) {
this.instance.getMetadataMap().put("configPath", prefix);
}
}
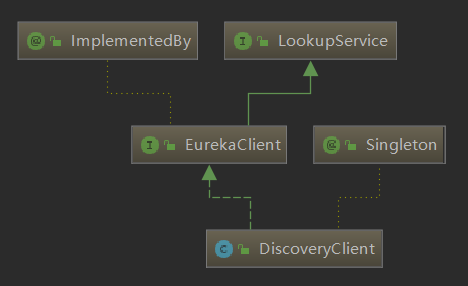
}上面的 init() 方法中依赖 EurekaClient.class,EurekaClient 主要是一个接口,该接口定义了 Eureka 客户端的主要功能,并定义了默认实现类 DiscoveryClient,代码如下:
@ImplementedBy(DiscoveryClient.class)
public interface EurekaClient extends LookupService {
//...
}
@Singleton
public class DiscoveryClient implements EurekaClient {
//...
}该类包含了 Eureka Client 向 Eureka Server 的相关方法。并且它是一个单例模式,而 EurekaClient 又继承了 LookupService 接口。它们之间的关系如图所示:
以上是 @EnableDiscoveryClient 的启动逻辑,从 EnableDiscoveryClient 的注释中我们可以看到,它最终主要是用来开启 com.netflix.discovery.DiscoveryClient 的实例。从该类的注释可以看出,该类包含服务注册、服务续约、服务下线、获取服务等功能。









