MyBatis的Sqlsession对应着一次数据库会话(即一次数据库连接)。由于数据库会话不是永久的,因此Sqlsession的生命周期也不应该是永久的。相反,在你每次访问数据库时都需要创建它(当然并不是说在Sqlsession里只能执行一次sql,你可以执行多次,当一旦关闭了Sqlsession就需要重新创建它)。创建Sqlsession的地方只有一个,那就是SqlsessionFactory的openSession方法。
在学习SqlSession实现原理之前,我们可以回顾一下SqlSessiom的用途,在MyBatis中所有与数据库交互的操作(insert、update、delete和update)都是使用SqlSession进行执行的,因此我们有必要知道SqlSession是怎样运行的。
MyBatis的Sqlsession对应着一次数据库会话(即一次数据库连接)。由于数据库会话不是永久的,因此Sqlsession的生命周期也不应该是永久的。相反,在你每次访问数据库时都需要创建它(当然并不是说在Sqlsession里只能执行一次sql,你可以执行多次,当一旦关闭了Sqlsession就需要重新创建它)。创建Sqlsession的地方只有一个,那就是SqlsessionFactory的openSession方法。
SqlSession和SqlSessionFactory的关系如下图:
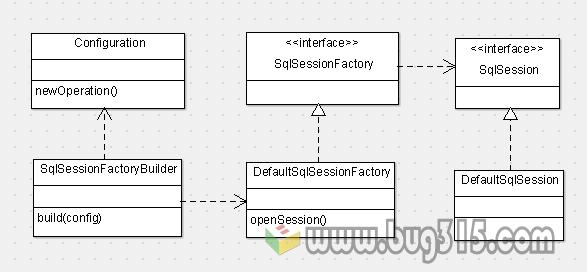
其中:
Configuration类表示MyBatis的配置文件
SqlSesionFactoryBuilder类用来创建SqlSessionFactory对象(即默认的DefaultSqlSessionFactory)
SqlSessionFactory这用来创建SqlSession对象
上面提到了SqlSession是通过SqlSessionFactory的openSession()方法创建的,下面是openSession方法的源码:
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
// 通过数据源的方式创建SqlSession实例
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType,
TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory =
getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(
environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType, autoCommit);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx);
// may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}从上面可以看出实际创建SqlSession的方法是openSessionFromDataSource()私有方法,创建sqlsession经过了以下几个主要步骤:
(1)从配置中获取Environment;
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
(2)从Environment中取得DataSource;
(3)从Environment中取得TransactionFactory;
(4)从DataSource里获取数据库连接对象Connection;
(5)在取得的数据库连接上创建事务对象Transaction;
(6)创建Executor对象(该对象非常重要,事实上sqlsession的所有操作都是通过它完成的);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType, autoCommit);
(7)创建sqlsession对象。
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor);
mybatis广告位
Executor的创建
Executor与Sqlsession的关系就像市长与书记,Sqlsession只是个门面,真正干事的是Executor,Sqlsession对数据库的操作都是通过Executor来完成的。与Sqlsession一样,Executor也是动态创建的:
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction,
ExecutorType executorType, boolean autoCommit) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
// 批量操作
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
// 普通的Executor
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 是否开启缓存
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor, autoCommit);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}可以看出,如果不开启cache的话,创建的Executor只是3中基础类型之一:
(1)BatchExecutor专门用于执行批量sql操作;
(2)ReuseExecutor会重用statement执行sql操作;
(3)SimpleExecutor只是简单执行sql没有什么特别的;
开启cache的话(默认是开启的并且没有任何理由去关闭它),就会创建CachingExecutor,它以前面创建的Executor作为唯一参数。CachingExecutor在查询数据库前先查找缓存,若没找到的话调用delegate(就是构造时传入的Executor对象)从数据库查询,并将查询结果存入缓存中。
Executor对象是可以被插件拦截的,如果定义了针对Executor类型的插件,最终生成的Executor对象是被各个插件插入后的代理对象。
Mapper
Mybatis官方手册建议通过mapper对象访问mybatis,因为使用mapper看起来更优雅,就像下面这样:
session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserDao userDao= session.getMapper(UserDao.class);
UserDto user =new UserDto();
user.setUsername("iMbatis");
user.setPassword("iMbatis");
userDao.insertUser(user);那么这个mapper到底是什么呢,它是如何创建的呢,它又是怎么与sqlsession等关联起来的呢?下面为你一一解答。
创建Mapper
表面上看mapper是在sqlsession里创建的,但实际创建它的地方是MapperRegistry:
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
if ( !knownMappers.contains(type) )
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " isnot known to the MapperRegistry.");
try {
return MapperProxy.newMapperProxy(type, sqlSession);
} catch (Exceptione) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}可以看到,mapper是一个代理对象,它实现的接口就是传入的type,这就是为什么mapper对象可以通过接口直接访问。同时还可以看到,创建mapper代理对象时传入了sqlsession对象,这样就把sqlsession也关联起来了。我们进一步看看MapperProxy.newMapperProxy(type,sqlSession);背后发生了什么事情:
publicstatic T newMapperProxy(Class mapperInterface, SqlSession sqlSession) {
ClassLoader classLoader = mapperInterface.getClassLoader();
Class[] interfaces = new Class[]{mapperInterface};
MapperProxy proxy = new MapperProxy(sqlSession);
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, proxy);
}看起来没什么特别的,和其他代理类的创建一样,我们重点关注一下MapperProxy的invoke方法
MapperProxy的invoke
我们知道对被代理对象的方法的访问都会落实到代理者的invoke上来,MapperProxy的invoke如下:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable{
if ( method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class ) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
}
final Class declaringInterface = findDeclaringInterface(proxy, method);
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(declaringInterface, method, sqlSession);
final Objectresult = mapperMethod.execute(args);
if ( result ==null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() &&
!method.getReturnType().equals(Void.TYPE) ) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + method.getName() +
"'(" + method.getDeclaringClass() +
") attempted toreturn null from a method with"+
" a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}可以看到invoke把执行权转交给了MapperMethod,我们来看看MapperMethod里又是怎么运作的:
public Object execute(Object[] args) {
Objectresult = null;
if(SqlCommandType.INSERT == type) {
Objectparam = getParam(args);
result= sqlSession.insert(commandName, param);
} else if(SqlCommandType.UPDATE == type) {
Object param = getParam(args);
result= sqlSession.update(commandName, param);
} else if(SqlCommandType.DELETE == type) {
Objectparam = getParam(args);
result= sqlSession.delete(commandName, param);
} else if(SqlCommandType.SELECT == type) {
if (returnsVoid &&resultHandlerIndex != null) {
executeWithResultHandler(args);
} elseif (returnsList) {
result = executeForList(args);
} elseif (returnsMap) {
result = executeForMap(args);
} else {
Object param = getParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(commandName, param);
}
} else {
thrownewBindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + commandName);
}
return result;
}可以看到,MapperMethod就像是一个分发者,他根据参数和返回值类型选择不同的sqlsession方法来执行。这样mapper对象与sqlsession就真正的关联起来了。
点击学习 MyBatis 教程,了解更多的 MyBatis 知识!







